Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Psychological Effects of Natural Colors – Introduction
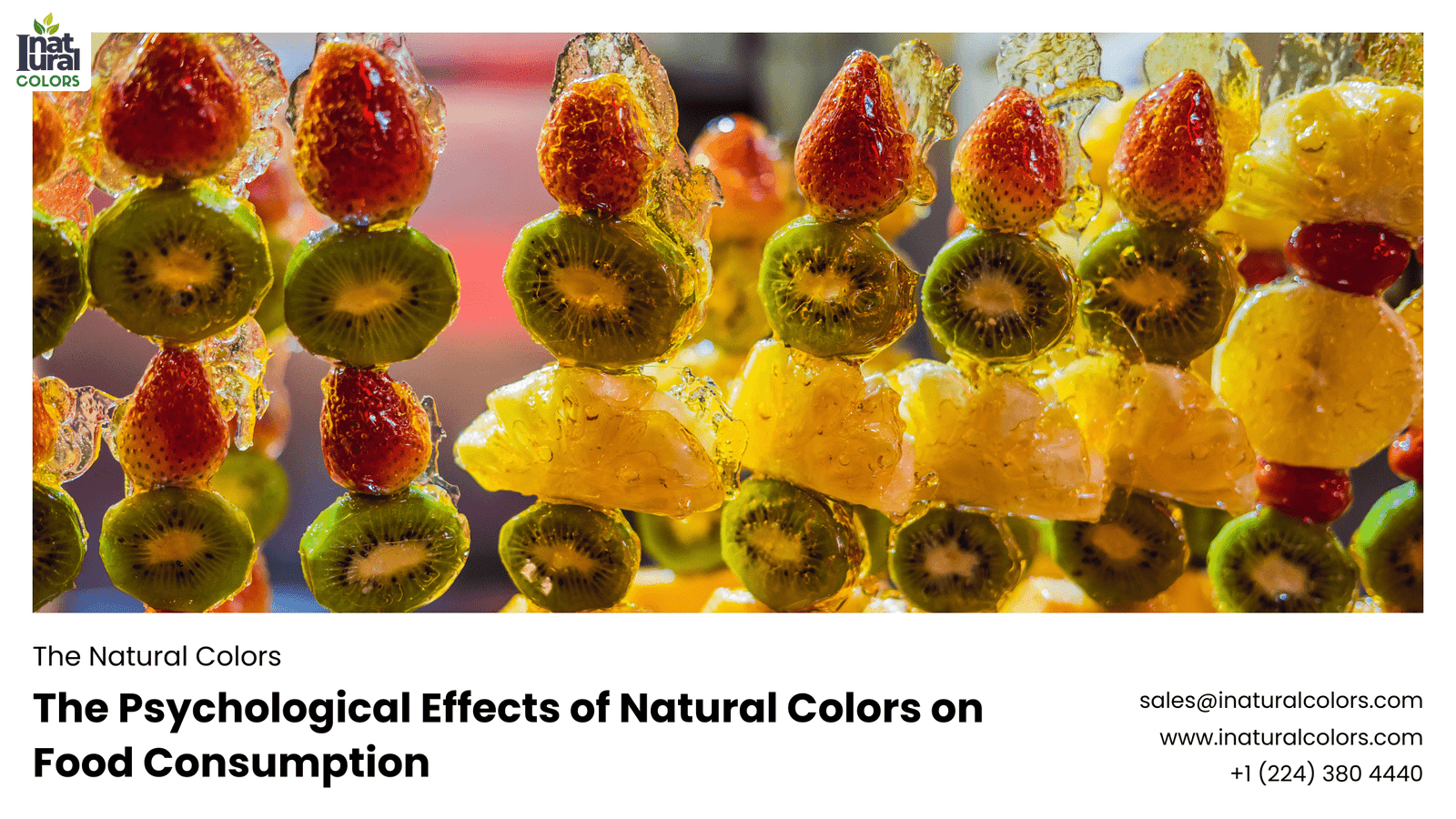
Why do you reach for that bright red apple or feel tempted by a yellow banana? It’s not just about taste; it’s about the colors. The natural colors in our food play a significant role in how we perceive and consume it. From influencing our appetite to shaping our food choices, the colors found in nature have a profound psychological impact on us. This article delves into the fascinating world of natural food colors and their effects on our eating habits.
Understanding Natural Colors
Definition of Natural Colors
Natural colors are derived from plants, minerals, and other naturally occurring substances. Unlike artificial colors, which are synthetically produced, natural colors come from sources like fruits, vegetables, and spices.
Common Natural Color Sources
Some popular sources of natural colors include:
- Red: Beets, strawberries, and tomatoes.
- Yellow: Turmeric, saffron, and yellow peppers.
- Green: Spinach, kale, and parsley.
- Blue: Blueberries and red cabbage.
Importance of Natural Colors in Food
Natural colors not only make food visually appealing but also often indicate the presence of beneficial nutrients. For example, the vibrant red of tomatoes signals the presence of lycopene, an antioxidant.
Psychological Effects of Colors
Overview of Color Psychology
Color psychology studies how different hues impact human feelings and behaviors. Colors can evoke emotions, affect moods, and even influence decisions, making them a powerful tool in various fields, including food consumption.
How Colors Influence Human Emotions and Behaviors
Colors like red can evoke excitement and energy, while blues tend to be calming. This psychological impact extends to how we perceive food. Bright colors can make food seem fresher and more appealing, thereby affecting our willingness to eat it.
Natural Colors and Appetite
How Different Colors Affect Appetite
Colors can significantly influence appetite. Warm colors like red, orange, and yellow are known to stimulate hunger, while cooler colors like blue and green can suppress it.
The Role of Color in Food Appeal
Food that is brightly colored and visually appealing is more likely to be chosen by consumers. This is because the brain associates vibrant colors with freshness and better taste.
Red and Its Impact
Psychological Effects of Red
Red is a powerful color that is often associated with passion, excitement, and energy. It can increase heart rate and stimulate the appetite, making red foods particularly appealing.
Red Foods and Their Appeal
Foods like strawberries, cherries, and tomatoes are not only delicious but also visually attractive due to their vibrant red color, which can make them more tempting to eat.
Yellow and Its Influence
Psychological Effects of Yellow
Yellow is a cheerful, happy color that can evoke feelings of warmth and positivity. It can also stimulate the appetite, making yellow foods more inviting.
Yellow Foods and Their Attractiveness
Bananas, corn, and lemons are examples of yellow foods that draw people in with their bright, sunny appearance.
Green: The Color of Health
Psychological Effects of Green
Green is often associated with health, tranquility, and nature. It has a calming effect and is frequently linked to foods that are fresh and nutritious.
Green Foods and Their Health Perceptions
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and broccoli are not only seen as healthy but are also appealing due to their fresh, vibrant green color.
Blue and Appetite Suppression
Psychological Effects of Blue
Blue is a rare color in the natural food world and is often associated with calmness and serenity. Interestingly, it has been found to suppress appetite, which is why it is rarely used in food marketing.
Blue Foods and Reduced Appetite
Blueberries are one of the few naturally blue foods. While they are nutritious and delicious, the color blue is not typically associated with hunger, which can reduce the amount of blue food consumed.
Natural vs. Artificial Colors
Differences Between Natural and Artificial Colors
Natural colors come from real food sources, while artificial colors are made from synthetic chemicals. Natural colors are often seen as healthier and safer, while artificial colors can sometimes cause allergic reactions and other health issues.
Consumer Preferences
Increasingly, consumers are preferring natural colors over artificial ones due to health concerns and a growing awareness of the benefits of natural ingredients.
Cultural Perspectives on Food Colors
How Different Cultures Perceive Food Colors
Cultural background can greatly influence how colors are perceived in food. For instance, in some cultures, white is associated with purity and is a popular food color, while in others, it may be linked to mourning and is less appealing.
Examples of Cultural Color Preferences in Food
In Japan, the color red is considered auspicious and is often used in festive foods, while in India, bright colors like yellow and orange, derived from spices, are common in many dishes.
Color in Food Marketing
How Color Is Used in Food Advertising
Marketers use colors strategically to make food more appealing. For example, red and yellow are often used in fast-food logos and packaging to stimulate appetite and attract customers.
Case Studies of Successful Color Marketing
Companies like McDonald’s and Coca-Cola use red in their branding to create a sense of excitement and energy, which helps in attracting consumers.
The Science Behind Natural Color Extraction
Methods of Extracting Natural Colors
Natural colors can be extracted using various methods, including boiling, crushing, and using solvents to draw out the pigments from plants and minerals.
Benefits of Using Natural Colors in Food Production
Using natural colors can enhance the nutritional value of food and reduce the risk of adverse health effects associated with artificial colors.
Health Benefits of Natural Colors
Nutritional Benefits of Naturally Colored Foods
Naturally colored foods are often rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can contribute to overall health and well-being.
Antioxidant Properties
Many natural colors come from substances that have antioxidant properties, helping to fight free radicals in the body and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Challenges in Using Natural Colors
Stability and Shelf Life Issues
Natural colors can be less stable than artificial ones, leading to issues with color fading over time. This can affect the appearance and appeal of food products.
Cost Implications
Natural colors can be more expensive to produce and use, which can increase the cost of the final product for consumers.
Future Trends in Natural Food Coloring
Innovations in Natural Color Extraction
Ongoing research is leading to new methods of extracting natural colors more efficiently and sustainably.
Predicted Consumer Trends
As consumers become more health-conscious, the demand for naturally colored foods is expected to continue growing, driving innovation and market growth in this sector.
Conclusion
Natural colors have a profound impact on our food choices and consumption habits. From stimulating appetite to evoking emotions, the colors found in nature play a crucial role in how we perceive and enjoy food. As the demand for healthier, more natural products increases, understanding the psychological effects of natural colors will become even more important for food producers and marketers.
FAQs
What are natural food colors?
Natural food colors are pigments derived from natural sources like fruits, vegetables, and minerals, used to color food without synthetic chemicals.
How do natural colors affect appetite?
Natural colors can influence appetite by making food more visually appealing, with warm colors like red and yellow typically stimulating hunger, while cool colors like blue can suppress it.
Why are natural colors better than artificial colors?
Natural colors are considered healthier as they come from real food sources and do not carry the same health risks as synthetic colors, which can sometimes cause allergic reactions and other issues.
How do cultural differences impact food color preferences?
Different cultures have varying associations with colors, which can influence their food preferences. For example, red is auspicious in Japan, making red foods popular, while bright colors are favored in Indian cuisine.
What are the future trends in natural food coloring?
Future trends include innovations in extraction methods and an increasing consumer preference for naturally colored foods due to growing health awareness.



